Deep within the brain lies a small, pea-sized organ known as the pineal gland. Often referred to as the “third eye,” this tiny structure plays a vital role in regulating your sleep-wake cycles by producing melatonin, a hormone that influences your circadian rhythm.
Beyond its biological functions, the pineal gland has long been shrouded in mystery. Many cultures and spiritual traditions associate it with intuition, higher consciousness, and the concept of the “third eye.” This connection has sparked curiosity and research into its potential to unlock deeper levels of awareness.
In this article, we’ll explore the anatomy and function of the pineal gland, its role in melatonin production, and the fascinating link to third eye activation. Whether you’re interested in science or spirituality, there’s much to discover about this intriguing part of the brain.
Key Takeaways
- The pineal gland regulates sleep by producing melatonin.
- It is often linked to the concept of the “third eye” in spiritual traditions.
- This small organ is located deep within the brain.
- Melatonin helps maintain your circadian rhythm.
- Research explores its potential role in higher consciousness.
Introduction to the Ultimate Guide on the Pineal Gland
Nestled in the center of the brain, the pineal gland plays a crucial role in regulating sleep. This tiny, pea-sized organ is often referred to as the “third eye” due to its mysterious connection to higher consciousness and intuition. But beyond its spiritual significance, it’s a powerhouse for maintaining your body’s internal clock.
This guide dives deep into the anatomy, functions, and secrets of this fascinating organ. You’ll learn how it produces melatonin, a hormone essential for your circadian rhythm. We’ll also explore its role in sleep patterns and its potential to unlock deeper levels of awareness.
Whether you’re curious about the science behind this gland or its mystical aspects, this guide has you covered. From its location in the brain to its impact on health conditions, we’ll uncover everything you need to know. Plus, we’ll share tips on how to naturally support its function for better sleep and overall well-being.
Ready to explore the secrets of the pineal gland? Let’s get started on this journey to understand one of the most intriguing parts of the human body.
Understanding Pineal Gland Function and Melatonin
Tucked away in the brain, this tiny organ plays a big role in your daily rhythm. It produces melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate your sleep and wake cycles. This process is essential for maintaining your circadian rhythm, the internal clock that keeps your body in sync.

Melatonin and Circadian Rhythm
Melatonin is often called the “sleep hormone.” It’s released in response to darkness, signaling to your body that it’s time to rest. This hormone helps you fall asleep and stay asleep, ensuring you wake up feeling refreshed.
Your circadian rhythm relies on melatonin to function properly. Without it, your sleep patterns can become irregular, leading to fatigue and other health issues.
Hormonal Secretion and Body Clock
The production of melatonin is a key part of your body’s hormonal system. It’s released in higher amounts at night and decreases during the day. This cycle helps your body know when to sleep and when to wake up.
Research shows that melatonin levels peak between 2:00 and 4:00 AM. This timing is crucial for maintaining a healthy sleep schedule.
Light Sensitivity and Dark Activation
Light plays a big role in melatonin production. Exposure to bright light, especially at night, can suppress its release. This is why dimming lights before bed can help you sleep better.
On the other hand, darkness triggers melatonin secretion. This natural response ensures your body is ready for rest when the sun goes down.
The Mystical Third Eye Concept Explored
Throughout history, the concept of the third eye has fascinated cultures worldwide. Often linked to the pineal gland, this idea symbolizes a gateway to higher consciousness and intuition. Ancient traditions, from Hinduism to Greek philosophy, have revered it as a source of spiritual insight.
René Descartes, the 17th-century philosopher, called the pineal gland the “seat of the soul.” He believed it connected the physical and spiritual realms. Ancient Greeks also saw it as a bridge between the mind and the divine, reinforcing its mystical symbolism.

The gland’s sensitivity to light adds to its spiritual allure. It produces melatonin, a hormone that regulates your sleep-wake cycles. This connection to light and darkness has led many to view it as a mediator between the physical and spiritual worlds.
“The third eye is not just a metaphor; it’s a portal to deeper understanding.”
Many believe that activating this organ can enhance spiritual perception. Practices like meditation, yoga, and breathwork aim to stimulate it, unlocking intuition and higher awareness. While science focuses on its role in hormone production, spirituality sees it as a key to unlocking inner wisdom.
Bridging science and spirituality, the third eye concept invites us to explore the mysteries of the brain and beyond. Whether you approach it from a scientific or spiritual angle, the idea of the third eye continues to inspire curiosity and wonder.
Anatomy, Structure, and Location of the Pineal Gland
Positioned deep within the brain’s core, this small organ holds a unique shape and function. Its pine cone-like appearance gives it a distinct identity among other brain structures. Located in the epithalamus, it sits near the center of the brain, surrounded by critical regions that influence its role in regulating bodily functions.
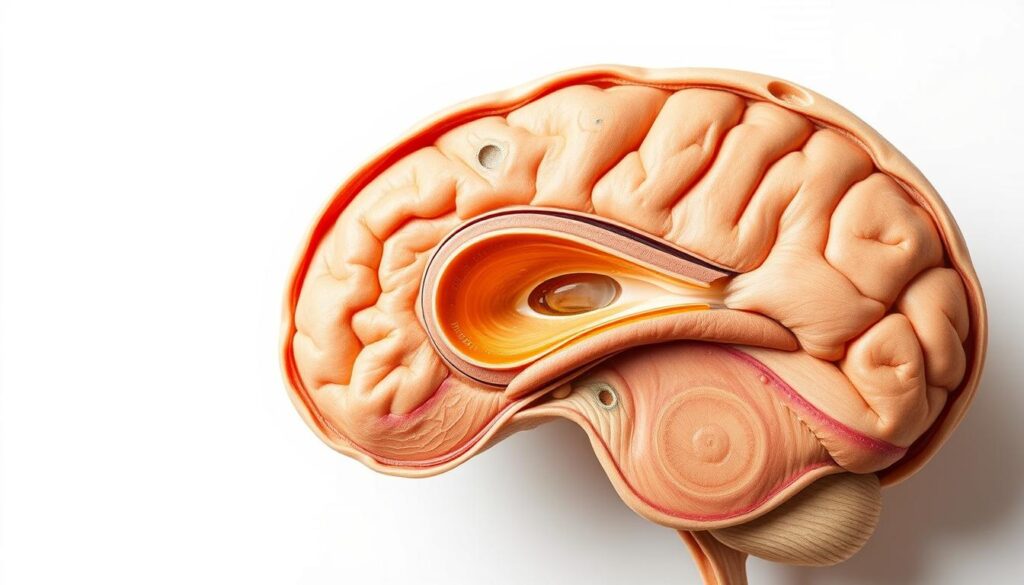
Physical Characteristics and Pine Cone Shape
The gland’s shape is one of its most striking features. Resembling a tiny pine cone, it measures about the size of a grain of rice. This unique structure is composed of specialized cells called pinealocytes, which produce melatonin, a hormone essential for regulating sleep cycles.
Surrounding these cells are supportive tissues that help maintain the organ’s function. Its compact size and shape make it a fascinating subject for both anatomical and spiritual studies.
Central Positioning in the Brain
Its central location in the brain underscores its importance. Situated near the thalamus and hypothalamus, it interacts with regions that control hormone secretion and circadian rhythms. This proximity allows it to play a key role in synchronizing the body’s internal clock.
Imaging tests, such as MRIs, often highlight its position using visible markers. These tools help researchers and doctors study its structure and function in detail. Understanding its anatomy provides insights into how it influences sleep, mood, and overall health.
Health Conditions Affecting the Pineal Gland
The pineal gland, though small, can face various health challenges that impact its function. From tumors to calcification, these conditions can disrupt its role in regulating sleep and overall well-being. Understanding these issues helps in recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment.
Pineal Gland Tumors and Cysts
Tumors in this area are rare but can have significant effects. They often cause symptoms like headaches, nausea, and vision changes. While some tumors grow slowly, others are aggressive and require immediate attention.
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like MRI, which provide detailed views of the brain. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, depending on the tumor’s type and severity.
Calcification, Trauma, and Injury Impact
Calcification is a common issue, especially as people age. It can impair the gland’s ability to produce melatonin, leading to sleep disturbances. Traumatic injuries to the brain can also affect its function, disrupting hormone secretion.
Regular check-ups and imaging tests can help monitor these conditions. Early detection and management are key to maintaining the gland’s health and ensuring proper sleep cycles.
How Pineal Gland Malfunctions Influence Hormone Levels and Sleep
When the pineal gland isn’t functioning properly, it can disrupt more than just sleep. This small organ plays a critical role in regulating melatonin, a hormone essential for maintaining your body’s internal clock. When its function is impaired, it can lead to imbalances that affect your overall health.
Sleep-Wake Cycle Disruptions
One of the most noticeable effects of a malfunctioning pineal gland is irregular sleep patterns. Melatonin production decreases, making it harder to fall asleep or stay asleep. This can lead to insomnia, fatigue, and a disrupted circadian rhythm.
Studies show that low melatonin levels are common in older adults, often causing sleep disturbances. This imbalance can also worsen conditions like jet lag or seasonal affective disorder (SAD), where light exposure further disrupts the body’s natural rhythm.
Cardiovascular and Mood Implications
Beyond sleep, a malfunctioning pineal gland can impact cardiovascular health and mood stability. Melatonin helps regulate blood pressure and heart function. When levels are low, it may increase the risk of hypertension and other heart-related issues.
Mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, are also linked to disrupted melatonin production. Sleep deprivation caused by low melatonin can worsen mental health, creating a cycle of poor sleep and emotional distress.
Understanding these effects highlights the importance of diagnosing and treating pineal gland dysfunctions. Whether through lifestyle changes or medical interventions, addressing the root cause can restore balance and improve overall well-being.
Exploring Natural Detox and Activation Methods
Many people are curious about natural ways to support the body’s internal clock and enhance overall well-being. Some believe that detoxifying and activating the pineal gland can improve sleep, intuition, and mental clarity. While these methods are popular in alternative medicine, it’s important to note that scientific evidence remains limited.

Detox Strategies for the Pineal Gland
Detoxification methods often focus on reducing substances that may impair the gland’s function. For example, limiting exposure to fluoride, found in tap water and toothpaste, is a common suggestion. Some also recommend dietary changes, such as reducing processed foods and increasing antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables.
Another popular approach is using supplements like Vitamin K2 or Vitamin D3, which may help reduce calcification. However, these strategies are largely anecdotal, and more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
Alternative Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle changes can also play a role in supporting the pineal gland. Practices like meditation and yoga are believed to enhance its activity by reducing stress and improving blood flow. Inversion postures, in particular, may increase circulation to the brain.
Controlling light exposure is another key factor. Reducing blue light from screens in the evening and spending time in natural sunlight during the day can help regulate melatonin production. These adjustments may improve your sleep-wake rhythm and overall health.
While these methods are promising, it’s essential to approach them with caution. Always consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle. For more insights on holistic health, visit our resource page.
The Role of Pineal Melatonin in Regulating Health
Melatonin, a hormone produced by the pineal gland, plays a pivotal role in maintaining health and well-being. This small but mighty organ helps regulate sleep, supports reproductive health, and even protects the cardiovascular system. Let’s explore how melatonin influences these critical areas.
Melatonin’s Effect on Sleep Patterns
Melatonin is often called the “sleep hormone” because it helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle. When darkness falls, your body releases more melatonin, signaling that it’s time to rest. This process ensures you fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer.
Disruptions in melatonin production can lead to sleep disorders like insomnia or irregular sleep-wake rhythms. Studies show that maintaining healthy melatonin levels is essential for a balanced circadian rhythm, which keeps your body in sync with day and night.
Interactions with Female Hormones and Reproduction
Melatonin also plays a role in female reproductive health. It interacts with hormones like estrogen and progesterone, influencing the menstrual cycle. Research suggests that melatonin levels fluctuate throughout a woman’s life, peaking before puberty and declining with age.
Low melatonin levels have been linked to irregular menstrual cycles and fertility issues. On the other hand, balanced melatonin production supports reproductive health and may even protect against certain hormonal imbalances.
Beyond sleep and reproduction, melatonin offers broader health benefits. It helps protect the cardiovascular system by regulating blood pressure and reducing inflammation. Studies also suggest that melatonin may guard against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Melatonin is more than a sleep aid; it’s a guardian of overall health.”
- Regulates sleep-wake cycles for better rest.
- Supports female reproductive health and hormone balance.
- Protects the cardiovascular system and reduces inflammation.
- May help prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
Understanding the dual role of melatonin in sleep and health highlights its importance. Whether you’re looking to improve your sleep or support your overall well-being, maintaining healthy melatonin levels is key.
Pineal Gland Research: Current Studies and Future Possibilities
Recent advancements in neuroscience have shed new light on the intricate functions of this small yet powerful organ. Researchers are uncovering its role in regulating sleep, mood, and even metabolic processes. These findings are paving the way for innovative treatments and deeper understanding.

One area of focus is the production of melatonin, a hormone essential for maintaining the body’s internal clock. Studies show that disruptions in melatonin levels can lead to sleep disorders and other health issues. For example, adolescents with impaired insulin metabolism often exhibit lower nocturnal melatonin levels, suggesting a link between this hormone and metabolic health.
Emerging research also explores the gland’s role in cardiovascular health. Melatonin has been shown to reduce inflammation and protect against endothelial cell dysfunction. In clinical trials, melatonin administration in COVID-19 patients reduced thrombotic events and mortality rates, highlighting its potential therapeutic benefits.
Innovative techniques like single-cell RNA sequencing are revolutionizing our understanding of this organ. Researchers have identified five major cell types, with pinealocytes making up 90% of the total. This breakthrough allows scientists to study how these cells interact and respond to external stimuli.
Future possibilities include developing targeted therapies for gland disorders. For instance, melatonin treatment in spinal cord injuries has shown promising results, improving blood vessel perfusion and motor neuron activity. These findings could lead to new treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and other conditions.
| Research Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Melatonin and Sleep | Disruptions in melatonin levels correlate with sleep disorders and metabolic issues. |
| Cardiovascular Health | Melatonin reduces inflammation and protects against endothelial dysfunction. |
| Single-Cell Analysis | Identified five major cell types, with pinealocytes comprising 90% of the organ. |
| Therapeutic Potential | Melatonin shows promise in treating spinal cord injuries and neurodegenerative diseases. |
As research continues, unanswered questions remain. For example, how does the gland’s sensitivity to light influence its function in different environments? What role does it play in aging and age-related disorders? These questions drive ongoing studies, offering hope for better diagnostic and therapeutic options.
In conclusion, the future of pineal gland research is bright. With cutting-edge techniques and a growing body of evidence, scientists are unlocking its potential to improve health and well-being. Stay tuned for more discoveries in this fascinating field.
Integrating Spirituality with Science: Activation Secrets
The pineal gland has long been a bridge between science and spirituality, sparking curiosity and debate. Ancient traditions revered it as the “third eye,” a gateway to higher consciousness. Modern science, on the other hand, focuses on its role in producing melatonin, a hormone essential for regulating sleep. This dual perspective makes it a fascinating subject of study.
Many believe that activating this small organ can enhance intuition and spiritual awareness. Practices like meditation, fasting, and sunlight exposure are often recommended. For example, meditation is said to stimulate the gland, while sunlight helps regulate melatonin production. These methods aim to align the body’s natural rhythms with higher states of consciousness.
Scientific research supports some aspects of these claims. Studies show that mindfulness meditation can reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality. Sunlight exposure is proven to boost melatonin levels, which are crucial for maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle. However, other activation methods, like fasting or herbal supplements, lack robust scientific evidence.
“The pineal gland is more than a biological organ; it’s a symbol of the connection between mind and spirit.”
Historical context adds depth to this discussion. Ancient Egyptians and Hindus viewed the gland as a spiritual center. René Descartes called it the “seat of the soul.” Today, this belief persists in practices like yoga and breathwork, which aim to activate the gland for deeper awareness.
Balancing science and spirituality is key. While some activation methods are backed by research, others remain speculative. Exploring both sides encourages a holistic understanding of this intriguing organ. Whether you approach it from a scientific or spiritual angle, the pineal gland continues to inspire curiosity and wonder.
Conclusion
The pineal gland, a small yet powerful organ, bridges science and spirituality in fascinating ways. It produces melatonin, a hormone essential for regulating sleep and maintaining your body’s internal clock. Disruptions in its function can lead to sleep disorders, mood imbalances, and even cardiovascular issues.
Health conditions like tumors or calcification can impair its ability to function properly. Ongoing research explores its role in metabolic health, cardiovascular protection, and even neurodegenerative diseases. This dual focus on science and spirituality continues to inspire curiosity and wonder.
Whether you’re drawn to its biological functions or its mystical symbolism, the pineal gland remains a captivating subject. Dive deeper into its mysteries to uncover how this tiny organ influences your health and consciousness.

